轻云pdf压缩编辑官网
本文共 341 字,大约阅读时间需要 1 分钟。
PDF文件作为日常办公中常用的文档格式之一,文档中可包含表格、图片、文字等内容,所以PDF文件体积通常会比较大。但是有时体积太大是个问题,这时候我们就需要压缩,那么用什么方法压缩pdf最好呢?今天小编就给大家介绍一个压缩pdf又好又快的方法:
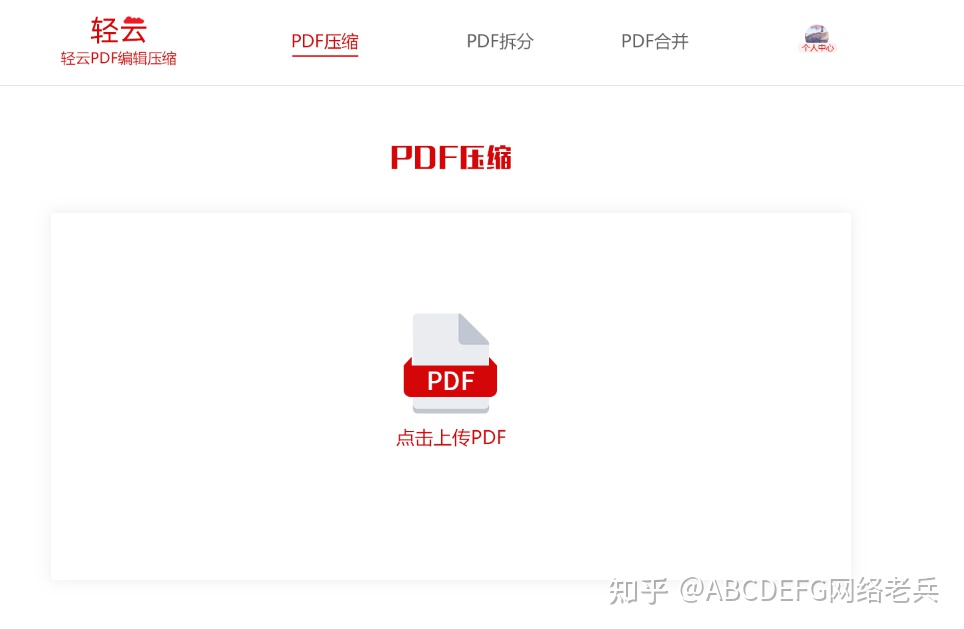
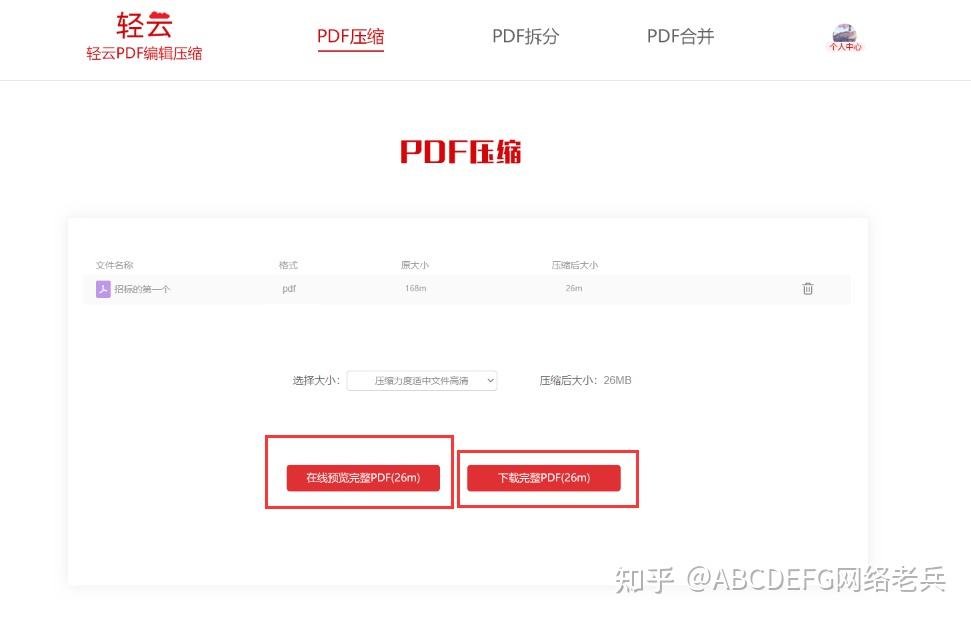
第一步:点击打开轻云pdf编辑压缩官网: www.qingyunpdf.com 打开轻云pdf编辑压缩官网,上传pdf文件,上传完毕后网站会自动压缩。
转载地址:http://yyav.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章